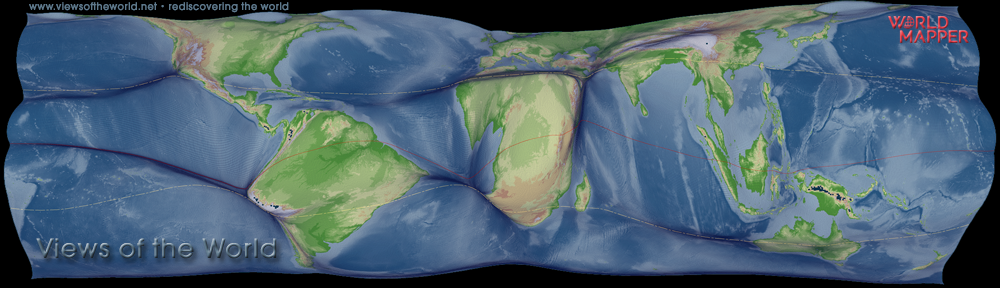
Maney, the publishers of the Cartographic Journal have today released their Maney Feature of the Month ‘Cartography & Surveying’ about cartography and surveying. Part of that feature is my contribution about some of the mapping results of my PhD research. It focuses on a series of maps that show the gridded cartogram technique applied to various themes from the human and physical environment, and briefly explains the underlying method.
As this blog entry also happens to be the 100th post on the Views of the World website, I have created a new version of the gridded world population cartogram. The map shows our blue planet a little brighter than the version that I created for the Maney feature (which puts the main focus on the topographic display), and also displays the major rivers traversing the spaces of humanity as pulsing arteries of an essential element. This is the ‘Blue Human Planet’:
Tag Archives: environment
Views of the World at Night
The Sendai earthquake in Japan sparked a debate about sustainable energy supplies of industrialised countries – with a controversial discussion about the safety and sustainability of nuclear power. The book ‘Sustainable Energy – without the hot air‘ by David MacKay is an outstanding read in this regard, outlining the all key issues that matter for our future energy need (the digital version is free, although I recommend the paperback which can even be read without wasting any electricity).
Switching the lights off was not a matter of choice for many people in the North of Japan after the devastations of the earthquake also affected the energy supplies (not only because of the Fukushima accident, but also because of a widely destroyed basic infrastructure). Another image featured in the NASA Earth Observatory takes a closer look at the electricity losses that occurred after the Earthquake by creating a composite image of two images of lights observed in 2010 and after the earthquake at March, 12 this year. As a highly industrialised country, the illuminated areas in Japan usually show the places where people live (see worldmap below), while dark areas are the unpopulated regions, hence the reprojection on a gridded population cartogram results in a dominantly bright image. Using NASAs display of the electricity losses therefore gives a good representation of the number of people affected by the power losses (and largely also the Tsunami and Earthquake itself) in the Northeast: The redrawn version of the image shows these as the red areas, while the brighter yellow areas in the South and West show the regions that has a similar illumination compared to the previous image. This is how ‘Japan at Night’ looked after the 2011 Earthquake:
 Continue reading
Continue reading
World Water Day
Water is a basic requirement for all life, yet water resources are facing increasing demands from, and competition among, users. In 1992, the UN General Assembly designated 22 March of each year as the World Day for Water
(quoted from the WWD website).
Water is more than a chemical substance contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms. Water has become a reason for conflicts and a controversial commodity, and yet, it is inevitable for every human being on the planet. The range of issues that are important when looking at water is diverse, and all fields reveal the global inequalities in access to clean water. One of these issues is the commercialisation of water, which on a global scale finds its manifestation in the bottled water industry: Bottled water is one way of getting access to clean water if there is no reliable central water supply or local source of water.
Edward Stanley from University College London looked at the bottled water business for a Geography dissertation project, for which I created some worldmapper maps visualising his data from that research on ‘Commodification and Mass Consumption – The Case for Bottled Water‘.
The topics that we mapped focus on the countries of origin of the globally operating bottled water companies and the bottled water consumption in the world. The first map shows the total bottled water consumption including a world population cartogram as a reference. In addition, the countries are shaded by their per capita consumption of bottled water (a worldmapper-style version of this map is shown at the bottom of this page):
Map I: Global Bottled Water Consumption (total and per capita) (click for larger view)
(click for larger view)
The International Year of Forests 2011
 The United Nations General Assembly declared 2011 as the International Year of Forests (IYF) to raise awareness on sustainable management, conservation and sustainable development of all types of forests. The British Prime Minister Cameron experienced, how forests can become a very political issue, which shows how emotional people’s attitude towards their environment can sometimes become. The International Year of Forests, however, was never mentioned in the debate that went on during the proposed forest sell-off by the British government, which highlights one of the problems that sometimes these proposed International-Years-of-Something face: A lack of attention. On a global scale, 31% of the land area is covered by forests. Some of these areas are highly under threat by unsustainable forestry and environmental pollution. The IYF therefore is meant to emphasise “the need for sustainable management of all types of forests, including fragile forest ecosystems” (UN resolution on the IYF). Continue reading
The United Nations General Assembly declared 2011 as the International Year of Forests (IYF) to raise awareness on sustainable management, conservation and sustainable development of all types of forests. The British Prime Minister Cameron experienced, how forests can become a very political issue, which shows how emotional people’s attitude towards their environment can sometimes become. The International Year of Forests, however, was never mentioned in the debate that went on during the proposed forest sell-off by the British government, which highlights one of the problems that sometimes these proposed International-Years-of-Something face: A lack of attention. On a global scale, 31% of the land area is covered by forests. Some of these areas are highly under threat by unsustainable forestry and environmental pollution. The IYF therefore is meant to emphasise “the need for sustainable management of all types of forests, including fragile forest ecosystems” (UN resolution on the IYF). Continue reading
Demographic Change in the UK and the Environment
 The new 29th report by the Royal Commission on Environmental Pollution explores the environmental challenges faced by the UK as a result of demographic change. The cover of the report features my population cartogram of the United Kingdom surrounded by the commissions royal blue (see larger image of the cover map here). The report also happens to be the last work of this Royal Commission, which together with several other Defra bodies will be abolished later this year in its 31st year of existence.
The new 29th report by the Royal Commission on Environmental Pollution explores the environmental challenges faced by the UK as a result of demographic change. The cover of the report features my population cartogram of the United Kingdom surrounded by the commissions royal blue (see larger image of the cover map here). The report also happens to be the last work of this Royal Commission, which together with several other Defra bodies will be abolished later this year in its 31st year of existence.
Yesterday’s (16/02) official launch of this report in London was accompanied by a vigorous debate about the key findings, with much of the discussion being closely related to the demographic trends in the United Kingdom and which implications these have. Continue reading
Global Water Insecurity
Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity is the title of a new study that points out that almost 80% of the world’s population are exposed to some risk of insecure freshwater resources (published in Nature 467, 555-561 (30 September 2010) | doi:10.1038/nature09440). The researchers created a global raster plotting the security level of water resources based on an index of water threats which is discussed in their paper.
Much of the threats in wealthier countries can be counteracted with technology, which explains much less actual insecurity in these countries – but therefore puts biodiversity at risk and resulting in a high price for an inevitable resource of human life.
Talking to BBC News Peter McIntyre from the University of Wisconsin, one of the scientists involved in the study, puts it this way:
“But even in rich parts of the world, it’s not a sensible way to proceed. We could continue to build more dams and exploit deeper and deeper aquifers; but even if you can afford it, it’s not a cost-effective way of doing things.” (Source: BBC)
The unaltered stress level of global freshwater resources as published in the study is presented in this map (Source: Nature):

Accompanied by the map of biodiversity, this gives an interesting insight to the impacts on biodiversity. The impact on human population remains less shown in this depiction but is another crucial issue of the paper. As mentioned before, 80% of the world population are exposed to threatened water resources. By applying their map to the gridded-cartogram technique, the whole impact of these threatened water resources on the population becomes apparent. The 80% at risk become visible, as the map transformation preserves the geographical reference of the underlying grid. The emerging picture is going along quite well with the findings of the study and thus adds another interesting perspective on the issue of threatened water resources in the most populated regions in the world. All data from the study is available on http://www.riverthreat.net/data.html and we used that data to reproject the key maps of the study.
This map shows the “natural” picture of the human water security threat level from the study:
When taking the investments on water technology into account, this picture changes considerably, as the next map shows: