This is the Icelandic version of a poster on mapping wilderness and remote areas created for the the 2016 Science Day at the University of Iceland (Vísindadagur Verkfræði- og náttúruvísindasvið, Háskóli Íslands):
Víðerni og afskekkt landsvæði ná yfir margbreytileg svæði á yfirborði jarðar. Slík svæði eru strjálbýl og eru að hluta til afsprengi af skipulagi sem hvetur til þéttingar byggða. Yfir helmingur jarðarbúa í dag býr á svæðum sem skilgreind eru sem borgir, og meira en 95% jarðarbúa býr á um 10% af yfirborði lands. Hin 90 prósentin eru þó fjarri því að vera einsleit víðernissvæði, Það eru mismunandi skoðanir á því hvort og þá hvernig eigi að nýta hin óbyggðu svæði heims.
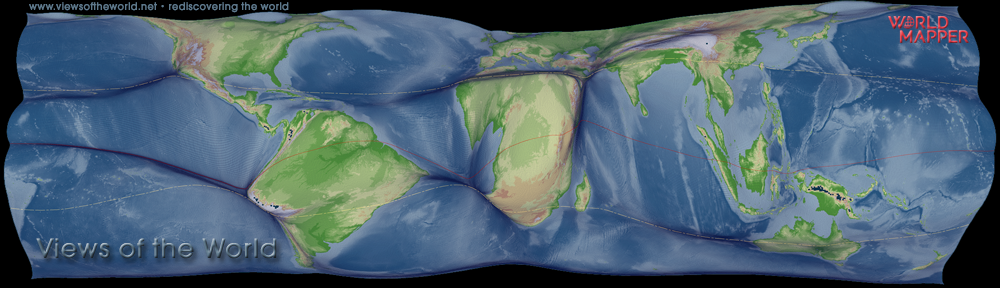
Aðeins um 15% fólks í ríkari hluta heimsins býr í meira en klukkustundar fjarlægð frá næstu borg. Í fátækari hluta heimsins er hlutfallið 65%. Hér er kynnt nýstárleg nálgun á myndrænni framsetningu og skilningi á hinum afskekktu landsvæðum jarðar sem eru að líkindum hennar síðustu víðerni. Notuð er tækni sem kalla má „bjöguð hnitvörpun“ (gridded cartogram transformation). Tæknin er notuð til kortleggja hversu fjarlæg svæði eru í hugum meirihluta mannkyns. Niðurstöður sýna umfang afskektra svæða eins og það birtist með tilliti til ferðatíma til næstu borgar, hvort sem er yfir land, vötn eða sjó. Stærð hverrar svæðiseiningar byggir á útreikningi þess tíma. Kortið gefur afskekktum svæðum aukið rými og veitir nýja sýn á svæðisbundið umfang afskekktra svæða í hlutfalli við þéttbýl svæði.
Tag Archives: wilderness
Visualising wilderness

(click for larger version – high resolution PDF)
Following an article on IFL Science (which itself followed a recent online and print article in Popular Science) here comes some further background and material from my work on visualising travel times to the nearest large cities Continue reading
Where the Wild Spaces Are: Un planeta salvaje
Make the world a wilder place | Por un planeta más salvaje

Wilderness and remote areas are a diverse element in the patchwork of spaces that form the land surface of our planet. Only very small amounts of people are living in sparsely populated areas, which is an expression of the strong organisation of human societies to maximise those living in close relative proximity. More than half of the world’s population now lives in areas categorised as cities, and although more than 95% of the world’s population live in approximately only 10% of the land area, the remaining 90% of space on land are far from being uniform remote or even wild areas.
There are very different ways of how the un-built area that still makes the largest share of land can be understood in terms of being under influence and in reach of human civilization. Only 15% of people in rich countries live more than an hour of travel time from a city (of at least 50,000 people), while the same applies to 65% of people living in the poor countries of the world. This paper demonstrates a different approach to visualising and understanding these loneliest places on the planet by using a technique called a gridded cartogram transformation. The following map shows a gridded cartogram visualising the relative distance of areas to the majority of people. The maps derived from the distorted grid show the physical space transformed according to the absolute travel time that is needed to reach the nearest major city by land transport averaged over the area of a grid cell, resulting in a map that gives the remotest places most space and provides a unique new perspective on the spatial dimension of remoteness: