A little bit from my archives which I never got around putting online before…here it comes: Last September I was invited to do a keynote at FOSS4G, OSGeo’s Global Conference for Open Source Geospatial Software. The event is the annual gathering of Open Source Geospatial Developers, Users and Leaders and was held at Nottingham’s new East Midlands Conference Centre, 17th to 21st September. The conference motto was ‘Geo for all’ because, as the organisers explain, “many people who work with geo software and maps find themselves becoming passionate advocates for the power of geography to make a difference: in government, business, travel, environment, crime reduction, social justice and communications to name just a few domains. Open Source Geo software makes this possible.”
So how does a geographer, working with geospatial software but being less so a developer, address a huge crowd of people who are little reluctant to see themselves as geeks and nerds? Instead of pretending to be as clever as most of the audience I took a slightly different stance, trying to bridge the gap between those on the programming side and those on the applied side – two groups which sadly rarely speak to each other. Traditional cartographers often see their field of work undermined (and threatened) by computerised methods to generate mapping products, while coders very often find the obsession with minute detail and ‘artisan’ cartography annoying. If the two worlds would come a bit closer together, and both sides speak a bit more with each other, the world of cartography and geospatial visualisations could benefit so much more. Addressing a more technical audience, I concluded that we should all think a little bit more before we start mapping, and that we should give a good mapping project a little bit more time than we often do these days – but more importantly of course: We should never stop mapping. These are the slides of my talk, of course including many maps:
Category Archives: conferences
Where the Wild Spaces Are: Un planeta salvaje
Make the world a wilder place | Por un planeta más salvaje

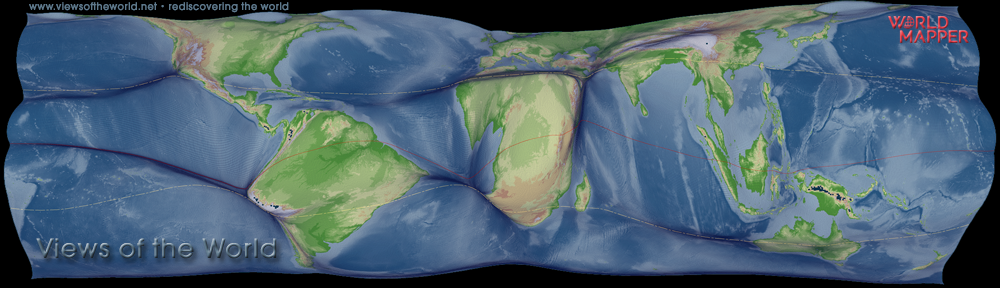
Wilderness and remote areas are a diverse element in the patchwork of spaces that form the land surface of our planet. Only very small amounts of people are living in sparsely populated areas, which is an expression of the strong organisation of human societies to maximise those living in close relative proximity. More than half of the world’s population now lives in areas categorised as cities, and although more than 95% of the world’s population live in approximately only 10% of the land area, the remaining 90% of space on land are far from being uniform remote or even wild areas.
There are very different ways of how the un-built area that still makes the largest share of land can be understood in terms of being under influence and in reach of human civilization. Only 15% of people in rich countries live more than an hour of travel time from a city (of at least 50,000 people), while the same applies to 65% of people living in the poor countries of the world. This paper demonstrates a different approach to visualising and understanding these loneliest places on the planet by using a technique called a gridded cartogram transformation. The following map shows a gridded cartogram visualising the relative distance of areas to the majority of people. The maps derived from the distorted grid show the physical space transformed according to the absolute travel time that is needed to reach the nearest major city by land transport averaged over the area of a grid cell, resulting in a map that gives the remotest places most space and provides a unique new perspective on the spatial dimension of remoteness:
The Visualisation of Spatial Social Structure: Reflections on Critical Methods
‘(How) do we understand Capitalism? Reflections on critical methods’ was the title of a workshop on critical methods at the University of Manchester (September 13-14th). As the announcement of the workshop states, ‘there is no consensus on what critical social science is, exactly. Largely it is defined as not orthodox economics or positivist social science‘. Continue reading
From geovisualisation to neocartography: Maps in a digital world

Changing technologies have always had a considerable impact on cartography and continue to do so. Several technological revolutions marked important steps in the practice and process of creating maps. Mechanical, optical and photo-chemical technologies changed the way maps were produced. Then, the discovery of electronic capabilities made a new dimension in map production accessible: Not only most of the design techniques were transferred to digital platforms, used at some step in the production of almost all maps created today, but also the possibility to deal with huge amounts of data that can hardly be analysed by a single person enables cartographers to find ways to automate data processing for cartographic visualisation. This is where the term neocartography comes into play, which gives credit to the most recent trends in the field of map-making. Continue reading
Global Spaces of Food Production
Featured

In the year 2000 there were approximately 15 million square km of cropland and 28 million square km of pasture which are represented in the two main maps. These are equal to 12% respectively 22% of the ice-free land surface. This is according to estimates of a study on the geographic distribution of global agricultural lands by Ramankutty et al (published in Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2008) who used a methodology of combining agricultural inventory data and satellite-derived land cover data to come to these figures (data can be accessed via Columbia University’s SEDAC). Continue reading
Down to Earth: 32nd International Geographical Congress
 The world of geography is coming together in the German city of Cologne (Köln) for the 32nd International Geographical Congress. The IGC is the quadrennial meeting of the International Geographical Union (IGU). Continue reading
The world of geography is coming together in the German city of Cologne (Köln) for the 32nd International Geographical Congress. The IGC is the quadrennial meeting of the International Geographical Union (IGU). Continue reading